


Magic 7.2 Download
Compiling and Installing Magic 7.2
GNU Autoconf Compilation "configure" Hints
Compilation "make config" Hints
Magic 7.2 Command-Line Syntax
Debugging Runtime Errors under Tcl
Version 7.2 Disclaimers
Version 7.2 Screenshot
Description of Version 7.2 Revisions
Features Specific to Magic Version 7.2
Features Specific to the Tcl Interpreter-Based Version
Using IRSIM with Tk/Tcl-based Magic
Things To Do
Bug Fixes
I have been working hard on the next-generation "magic" product. While it is in no condition to be called stable, it is a working product and so I am releasing it as BETA code. This is an upgrade from the previous designation as ALPHA code, as several chips have been successfully designed and manufactured using version 7.2. For differences between the 7.1 CVS source version available from Cornell and the 7.2 development version posted here, please see the following sections.The new development version is 7.3, with the introduction of a complete overhaul of the way magic deals with contacts, allowing arbitrary stacked contacts. Currently this is in a ALPHA state. Information on this version can be found at the Magic 7.3 page.
Revision 36 was reposted on 4/21/03, as I fixed a bug in the extract section which was producing incorrect length and width values for any transistors extracted with technology files not using the new "device" keyword (which is basically all of them except for the default one that comes with the source). The revision number is not updated because I have Revision 37 still on my laptop at home, but did not have the chance to transfer it to my web host yet. However, the fix is critical for correct circuit extraction; otherwise, area and perimeter values are interpreted as length and width on read-in, producing poor results (to say the least).
Revision 37 introduces autoconf to magic. Inevitably, this will produce a whole new round of porting problems for Solaris, Cygwin, OS X, etc. However, once the essential bugs are ironed out, it should result in fewer porting problems overall. For the moment, both configure and make config methods are retained.
Revision 49 changes the "varargs" method to "stdarg" (one of the items in "TODO"). This became urgent when the latest version of gcc claimed not to support the varargs method for variable arguments any more. HOWEVER, the stdarg method is different on different operating systems. The GNU autoconf system checks for this. The original "make config" script does not. In "make config", the correct setting is made for Linux. However, until some bug reports come back, I'm not certain which systems this will or will not compile on.
Revision 55 incorporates a port to the 64-bit Linux platform. Correct operation has been confirmed on an AMD Opteron machine running RedHat GinGin64 (2.4.20 kernel), loading a design with a half-million standard-cell gates and a half-million nets.
Download here:
File Revision Size Date magic-7.2.70.tgz 70 (4.1MB) May 13, 2004 magic-7.2.68.tgz 68 (4.1MB) April 29, 2004 magic-7.2.54.tgz 54 (4.0MB) October 27, 2003 magic-7.2.45.tgz 45 (4.0MB) August 4, 2003 magic-7.2.26.tgz 26 (3.8MB) February 24, 2003 irsim-9.7.0.tgz 0 (523KB) November 13, 2004 irsim-9.6.11.tgz 11 (461KB) December 3, 2003 irsim-9.6.4.tgz 4 (764KB) February 19, 2003 netgen-1.2.6.tgz 6 (444KB) September 30, 2003 netgen-1.1.tgz 2 (417KB) January 13, 2003
See file README.Tcl in the source distribution for complete instructions on compiling the Tcl/Tk-based version of magic. For the impatient, the general rule is:There is an interactive configure script which goes through all of the option settings. Support for the interactive script is deprecated; use the GNU autoconf script. However, at this time, it still works:
% ./configure % make % make install Note that Magic version 7.2 compiled with Tcl makes use of the optional Tcl/Tk package "BLT". Magic will run fine without it (it detects its absence and works around it), but if you don't have it, you'll miss the "cell manager" widget with the hierarchical cell view. BLT can be downloaded from SourceForge at the following location: BLT Toolkit Project on SourceForge.
% make config % make % make install Installing irsim version 9.6:
IRSIM 9.6 is beta code. Compiled normally (i.e., without the Tcl interface), it should compile and run like the long-standing standard version 9.5. However, the "make" process has been substantially cleaned up, and making for various systems should be much simpler. The "make" process is now identical to that for magic. Start with "make config" and then follow the instructions. The Tcl version of Irsim compiles and runs, except that the "analyzer" graphic display is a work in progress. The Tcl version takes advantage of both the ability to script the simulation procedure, as well as having a better interface to magic.IRSIM 9.6 has not yet been converted to GNU autoconf compilation. This feature should be coming soon.
Note that the "user subcircuit" system has not been ported to the Tcl/Tk platform. My intention is to replace or augment the C-code based subcircuit system with a Tcl script-based version.
% make config % make tcl % make install-tcl
IRSIM revision history: Version 9.6
- December 2, 2002
Original release of IRSIM version 9.6 with TCL.- December 9, 2002
Fixes error with revision 1 in which compilation will fail if the "user subcircuit" option is selected. Also fixes a problem with the print output to the tkcon console, which was sending garbage for arguments in error messages.- December 24, 2002
Fixes a few problems with the standard (non-Tcl) compile (thanks to Mike Godfrey for the fixes).- February 19, 2003
Corrects problems with refreshing the "analyzer" window by threading the graphics interface. This also speeds up the graphics initialization. This fix is not relevant to the Tcl version.- March 12, 2003
Updates the "make config" process to match that for Magic-7.2 revision 29. As per the notices posted above, the fixes may actually break the compile for some systems.- March 24, 2003
- April 9, 2003
This version was never officially released.- March 31, 2003
- September 23, 2003
Attempt to update varargs. This was a no-go, and superceded by revision 10.- September 26, 2003
Updates the deprecated "varargs" variable argument method, allowing compilation with gcc version 3, and overloads the Tcl "clock" command such that input command files (especially pre-version-9.6 ones) can be run without substituting "irsim::clock" for "clock".- December 3, 2003
Additional updates, especially to remove text after all #endifs to stop the compiler from complaining.
Also, corrected an error with the non-TCL-based version compile involving routine lprintf().Installing netgen version 1.2:
I am in the process of updating and migrating Massimo Sivilotti's netlist-processing program "netgen" to Tcl/Tk. This program can read and write numerous netlist formats, though its main feature of interest is the netlist comparator, which I intend to integrate into magic as an interactive LVS system.The "make" process is now the same as that designed for both magic and IRSIM, making this start to look like a real suite of VLSI tools! Note that this has only been compiled under Linux, so other platforms may encounter problems and it may be necessary to hand-edit compile-time definitions in the "defs.mak" file. Version 1.1 revision 2 is left in the download file for anyone who finds that the newest "make config" script changes break the compile process.
Netgen revision history: Version 1.1
Netgen revision history: Version 1.2
- December 14, 2002
This is a first draft. Only a few things have been changed in this release other than the Tcl/Tk port. There is now support for capacitors, resistors, bipolars, poly-poly capacitors and resistors built with the pseudo-poly layer in magic, in the SPICE, sim, and ext format read routines. The Tcl version has a completely revamped command set, better matching the general practices of Tcl command syntax (mainly meaning commands are full words rather than single letters). In addition, the command sets for "netgen" and "netcmp" have been combined.- January 13, 2003
Massive speedup of several critical and badly-written functions; reduced from O(N^2) to O(N). The "compare" command is now virtually instantaneous. Commands "nodes" and "elements" now give more relevant information regarding specific points in the network. "sim" format retains position in the element names (for FET and FET-like elements) for convenient traceback to a layout or schematic.
- March 12, 2003
Fixes the the "make config" process for Tcl/Tk compile. Also, finished implementing the Tcl "log" command for log file output, and added the script-level "lvs" command to replace the original standalone program "netcomp".- March 24, 2003
Corrections to TCL command interface.- March 26, 2003
This version was never officially released.- March 31, 2003
Changes for interoperability with magic and IRSIM.- April 3, 2003
Changes to save position information in element names for transistors read from .sim files.- September 22, 2003
Added the capability to handle "M=" syntax in SPICE files for declaring multiple transistors with equal size and connections.- September 30, 2003
Fixed an unfortunate problem with the "lvs" script command in which it implies that circuits which pass the low-level connectivity comparison match correctly. In fact, these circuits may have errors. The fix checks this condition, performs the high-level resolution of automorphisms, and reports a final pass/fail condition.Using netgen:
The most common use of "netgen" is to make use of its network comparison feature to compare a layout generated from magic with "extract" and "exttosim" ("ext2sim" in the non-Tcl version) commands against a layout generated from a schematic (e.g., xcircuit). The command sequence in netgen to compare these two netlists is:Arguments circuit1 and circuit2 are filenames. They do not need to have the ".sim" extension but do need to contain any directory path components (relative to the current working directory).
- readnet sim circuit1
- readnet sim circuit2
- compare circuit1 circuit2
- permute
- run converge
For circuits which do not match, it will be necessary to run the command "verify" to look at the list of illegal elements and nodes.
Note that the "verify" command produces copious output. Generally, it is preferable to use the "log" command to dump this output to a file. The command "verify only" produces just one line stating whether or not the circuits match. The output can be terminated at any time with a Control-C interrupt into either the terminal or console windows.
Starting with version 1.2, there is a script-level command which performs the sequence of commands above. This command is:
Arguments circuit1 and circuit2 are exactly as described above. logfile is the file to dump all output, and defaults to "comp.out" if not specified. Note that certain useful information, such as the initial report on the two files, and the final "yea or nay" result, is duplicated both to the log file and to the console (or terminal) window.
- lvs circuit1 circuit2 [logfile]
GNU Autoconf Compilation: Hints for "configure"
The "make config" script is being phased out in favor of GNU Autoconf. As usual for Autoconf compilation, compile-time options can be queried by doing "configure --help". At this time, the Autoconf script is in the subdirectory scripts, requiring descending to that directory to do the configure step and ascending back to the top-level source directory to run make. Options mostly mirror the "make config" options. The major options are:All of the optional modules in magic can be enabled or disabled by individual switches on the command line. Generally speaking, these should be left alone.
- --help
List all of the compile-time options.- --prefix=DIR
Set the install destination to directory path DIR. The default installation destination is /usr/local. Magic will be installed in various subdirectories of the prefix, such as /bin for executables and /lib for run-time files (technology files, startup scripts, display settings, etc.). This is especially useful to install magic in a local directory to avoid requiring root privileges to install, or to install a test version of a new release of magic which won't conflict with any existing installed versions.- --with-tcl
Compile magic as an extension of the TCL scripting language. Generally, this is preferred, due to the large number of enhancements available under the TCL version (such as the GUI frontend). However, it is not enabled by default.- --with-opengl
Compile magic with the OpenGL graphics interface. This is added to the standard X11 interface as a runtime option. Magic defaults to the X11 interface; OpenGL can be used by specifying "-d OGL" on the command line at runtime. This option is preferred when OpenGL libraries are available, especially on systems with fast graphics and a hardware implementation of OpenGL on the video card. It is not enabled by default.Some systems may run into trouble with either the TCL interpreter or OpenGL if they are installed in unusual places. The autoconf script goes to great lengths to find them, but in case of failure, the location of files may be specified explicitly by passing an argument to autoconf.
- --enable-locking
Allow file locking for multiple-user environments. File locking allows layout databases to be accessed by multiple users. Only one user at a time may edit a layout file, preventing accidental overwrites. Because having this option turned on allows magic to create new directories for lock files, it is disabled by default. However, even with the option enabled, magic cannot create new directories unless a system-level directory "/usr/local/flock" has been created (it is not created by the install process). This directory must be world-writable.- --disable-calma
Disable the GDS module.- --disable-cif
Disable the CIF module. Note that this will also disable the GDS module, which depends on it.- --disable-client-render
Disable client-side rendering, when OpenGL has been selected as an optional graphics package. Some video drivers may not handle server-side rendering correctly, although this is pretty rare.- --disable-lef
Disable the OpenAccess LEF format module.- --disable-plot
Disable the plot module.- --disable-readline
Disable the "readline" package. Note that the Tcl-based version of magic does not use "readline", so this option has no effect in conjunction with option "--with-tcl".- --disable-threads
Disable the use of POSIX threads (pthreads) with the X11 graphics interface. This reverts back to the use of a forked "helper" program to capture graphics calls.- --disable-nonmanhattan
Disable the non-Manhattan geometry extensions.- --disable-route
Disable the various router modules (these can not be enabled or disabled individually).- --disable-rsim
Disable the IRSIM interface. Note that the Tcl-based version of magic interfaces with IRSIM through the interpreter, so this option has no effect in conjunction with option "--with-tcl".- --disable-new-macros
Disable the use of the new macros, reverting back to the macros used by magic versions 6.5 and earlier. Veteran users of Magic will probably prefer the older macros. The newer macro set, developed by Philippe Pouliquen, makes use of the keypad and cursor keys for directional actions such as "move" and "stretch". The older macro set mapped the keys "QWER" to directions.For even more obscure options which may effect compilation on peculiar systems, refer to the text dump from "configure --help".
- --with-tcl=DIR
Specifies the path to find the file tclConfig.sh.- --with-tk=DIR Specifies the path to find the file tkConfig.sh. This is unlikely to be necessary unless Tk has been installed in a different place from Tcl.
- --with-opengl=DIR
Specifies the path to find the include and library files for OpenGL.- --x-libraries=DIR
Specifies the path to find the X11 library files (e.g., libX11.so and so forth). This is usually not necessary but has been found to be necessary at least on RedHat GinGin64 (the 64-bit OS for the AMD Opteron processor), where the 64-bit X11 libraries are stored in /usr/X11R6/lib64/.A Note on Tcl/Tk: Compilation under Tcl/Tk is probably both the most common option and the most problematic. A number of standard OS distributions do not come with all the bits and pieces necessary to compile a Tcl/Tk extension. If this is the case, then you will see this when you do configure when it says:
checking for tclConfig.sh... no.Assuming that you really, really want the Tcl version of magic (and in my opinion, you really, really do), your best bet is to download, compile, and install new versions of Tcl and Tk. This is pretty straightforward. Get the latest version from the Tcl/Tk Developers Exchange (click on the download link up near the top). One important thing to know when compiling your own: The executables for "tclsh" and "wish" will be installed as "tclsh8.4" and "wish8.4" (or whatever is the current version number). "wish" is critical, because magic uses it. You will need to rename or remove any existing executable for wish, and then either rename "wish8.4" to "wish" or else create a symbolic link "ln -s wish8.4 wish" (preferred).For example, I have a RedHat system which came with Tcl/Tk 8.0 installed in /usr/bin/. Compiled from source, Tcl/Tk 8.4 installed by default in /usr/local/bin/. I changed "/usr/bin/wish" to "/usr/bin/wish8.0" and changed "/usr/local/bin/wish8.4" to "/usr/local/bin/wish" (hmm, did I just say "preferred"?).
Compilation: Hints for "make config"
Some of the configuration options may be obscure or require an explanation. In a nutshell, here are the options encountered in "make config" and what they mean. Note that not all of these options will necessarily be presented, depending on prior choices.
- CAD_HOME:
This is the default root directory of the installation (not the source). In days long past, it was standard practice to have a user named "cad" with its own home directory. When average disk space became large enough for mere users to compile and install their own magic distribution, it became necessary to be able to override the "cad" user directory with an environment variable. Now, unless you have some particular concern about keeping all CAD tool software in its own separate directory tree, the standard installation location is /usr/local. There is no need to set the environment variable CAD_HOME unless you want to want to have magic start up seeing a different set of runtime files (technology files, display definition files, interpreter scripts, etc.) than it was compiled/installed with.- Scripting language:
The original magic ran without any kind of interpreter environment. That is, magic's command set was the entire command set, with no ability to define procedures or write macros incorporating variables, loops, or conditionals. Rajit Manohar added the SCHEME interpreter in magic version 7.0. SCHEME is a subset of the LISP language. I added the Tcl interpreter into version 7.2. The Tcl interpreter is a somewhat better "fit" in that magic's original command interface is almost completely compatible with Tcl syntax. The interpreters are mutually exclusive. Note that SCHEME is embedded (the interpreter is compiled into the program), whereas the Tcl interpreter option makes magic an extension of the Tcl language (the interpreter is not compiled; magic runs the existing interpreter on startup and links its routines to it). Note that the subsequent "make" and "make install" become "make tcl" and "make install-tcl", respectively, when the Tcl option is chosen.- Window configurations:
Magic is set up to allow multiple graphics interfaces, selectable at runtime. Due to the overwhelming persistence of X11 on UNIX-based machines, X11 remains as the default option. OpenGL is preferred if you have a fast video card which can handle OpenGL calls and which is supported by the operating system. You can select more than one option; separate the numbers with spaces.- Operating systems:
Operating system choice is deprecated as of version 7.2 revision 35, which uses the autoconf OS and hardware detection script. For prior revisions:
Most operating systems are represented here. The development platform is RedHat Linux. Other OS versions may get broken occasionally, as the developers don't have a chance to test under all operating systems before posting a new distribution. Please report any problems immediately so they can be corrected.- Machine-specific switches:
Hardware choice is deprecated as of version 7.2 revision 35, which uses the autoconf OS and hardware detection script. For prior revisions:
If your machine is in the list, choose it. Otherwise, select "none of the above".- Client-side OpenGL:
This option only shows up if you have selected OpenGL as a graphics interface. Normally you should be able to choose "yes" and forget about it. However, the occasional video card OpenGL driver has problems with synchronizing client-side rendering. If portions of the layout start appearing in the wrong colors or styles, then client-side rendering is probably suspect.- Calma module:
Handle GDS input/output. This is a very small module, and there's no particular reason not to select it.- CIF module:
Handle CIF input/output. Since CIF and GDS are pretty much the only layout formats accepted by foundries, and the CIF module is required for GDS input/output anyway, always select "yes".- Plow module:
Beginning with revision 19, the "plowing" option (commands "plow" and "straighten") has been re-introduced as an option. Under the Tcl-based version of magic, an additional configuration option "module" is accepted, and will compile the "plow" feature as a separate, run-time loadable module. The module remains uninstalled until one of the two plowing commands is used, at which point it automatically loads and initializes itself. The modularity of the code is completely transparent to the end-user, apart from a diagnostic message to the effect that the loading and initialization has occurred and was successful. Normally, one would select whichever option is presented as default: "module" under Tcl, "yes" otherwise.- Plot module:
Handle plot output. Although for a while the only graphics options were obscure, the "pnm" and "postscript" options are available since magic version 7.1, and make the plot module useful to have around for generating hardcopy of layouts. "plot pnm" eliminates most layout details but interpolates colors where detail exceeds the pixel resolution of the output device. This is especially useful for large layouts. "plot postscript" captures all the detail of the magic layout and is more useful for small layouts. Available plot options are determined from the "plot" section of the technology file. "pnm" and "postscript" options are written into the default scmos technology file, but may need to be copied into other technology files (especially the MOSIS ones) to be able to use the plot command with those technologies.- File-locking:
File locking was incorporated by Michael Godfrey for support of multi-user projects, where several people may be working on a layout at one time and synchronizing the activity can be a problem. Read the documentation on file-locking in the magic source distribution for details; a system-level directory needs to be created before file-locking will be activated on magic startup. When active, any layout file which is being edited by one user, or has been loaded and contains changes to the layout, is marked as "locked" by that user, and can only be accessed as a "read-only" file until the lock is released. Users who do not expect to work on layout projects with multiple designers can select "no" for this option. However, as long as the system-level lock directory does not exist, there is no difference in the operation of magic regardless of whether file locking has been selected or not (except for magic version 7.1, which has a broken implementation and raises an error message on startup which can be safely ignored).- Readline:
"readline" is a UNIX package which adds command-line history, substitution, and word completion to any command-line-based program. The main useful feature with magic is the use of the up and down arrow keys to access the command history, and the use of the tab key for automatic command, filename, and cellname completion. See the "readline" documentation for a complete description of its capabilities. When selecting "yes", the configuration script looks for a system "readline" library in the usual places. If one exists, it is used in preference to the source version copied into the magic source distribution. This can be problematic, as certain routines used by magic may or may not exist in the system readline version. Magic version 7.2 accepts the answer "force", which forces magic to compile the built-in version of readline regardless of what libraries may exist in the system. The Tcl-based version relies on Tcl's command-line history, and does not include this option.- Threads:
This option enables threaded graphics. If not selected, a separate program called the "XHelper" is forked off of the main executable, allowing magic to accept input from both the graphics window and the command line. With the "threaded graphics" option enabled, magic runs the graphics input selection from a separate thread. The simplified communication makes the program startup much faster. Normally you should answer "yes". If the Posix threads ("pthreads") library does not exist or cannot be found on the system, the option will be disabled. The "threads" option is not relevant to the Tcl version of magic.- Nonmanhattan extensions:
Nonmanhattan extensions adds some capability to handle layout geometry with angles other than 90 degrees. Because this is alpha code, all layout containing non-Manhattan geometry written by magic should be checked by an independent program before shipping to a foundry. Commands "splitpaint" and "spliterase" are added for some limited handling of non-Manhattan geometry. CIF and GDS reads of non-Manhattan geometry will duplicate non-Manhattan structures if this option is on. If not selected, CIF/GDS reads of non-Manhattan structures will "stairstep" the input at the resolution of the internal grid. See the text file in the magic source distribution documentation for additional information.- Route module:
This single selection selects all of the route options available to magic. Note that there are quite a few of them, and most people consider them all to be substandard. They will do the job, though, if not prettily. See the magic tutorials for additional information on the various routing commands.- Rsim module:
This module lets magic operate interactively with the "IRSIM" digital simulation program. Note that the Tcl version of magic prohibits this option, as the Tcl version uses a different method to interface to IRSIM (currently, though, this interface is incomplete). See the magic tutorials for further information on simulation. The IRSIM source code is distributed separately from magic but is available on this page (see above).- New macros:
Most users learn to run magic with a combination of mouse operations, single-key macros, and command-line entry. The macro definitions are completely re-definable, but pretty much all users just learn to get along with the built-in definitions. However, there are two versions of these macros. The original ("old") macros match the ones claimed by the tutorials, and restrict usage to the standard keyboard keys, and restrict key combinations to shift and control. The new macros make use of function and keypad keys, as well as other combinations such as the alt key and the shift+control combination. People raised on the original macro set will probably be a bit disconcerted by the lack of the "q-w-e-r" mapping to west-south-north-east; however, the arrow keys and keypad keys make more sense, logically, and with a little practice, old habits can be replaced. Nevertheless, it remains up to the user to decide whether to choose "yes" or "no" here.
Basic usage:
magic [-noc[onsole]] [-w[rapper]] [-d devType] [-T technology] [file]
where:
-noconsoleComplete usage information:
(Tcl version only) Uses the calling terminal for terminal-based command-line input. Otherwise, a Tk console window is used.-wrapper
(Tcl version only) Magic layout windows use the GUI wrapper, including cell and technology manager windows, layer toolbar, and file menu.-d devType
-T technology
(all versions) Select the graphics interface at runtime. Specifying an invalid devType will result in a list of known types. The possible values of devType are determined at compile time, but the usual ones are NULL (no graphics), X11, and OpenGL. X11 is the usual default.
(all versions) Select the appropriate technology (.tech27) file. At present (this is on the to-do list), magic cannot change technology after startup. So the technology file corresponding to the layout to be loaded must be supplied to the command line at startup. The default technology is scmos, which is included with the magic source distribution. The complete list of available technology files depends on what has been installed on the system (see the technology file page for details).file
(all versions) Load the layout (.mag) file file into the layout window on startup.
magic [-noc[onsole]] [-w[rapper]] [-nowindow] [-d devType] [-T technology] [-m monType] [-D] [file]where the additional options not covered above are:
-nowindowObsolete usage information:
(Tcl version only) Run without displaying an initial layout window. This is used mainly for GUI wrapper scripts which like to generate and handle their own windows.-m monType
(obscure) monType names a monitor type. This is used in the search for the colomap file name, which is designated <tech>.<planes>.<mon>.cmap1. The default is "std" (corresponding to colormap file "mos.7bit.std.cmap1". The only other monitor type for which colormaps exist in the distribution is "mraster". This provides a way for users to override the system color assignments.-D
(all versions) Run in Debug mode.
magic [-g gPort] [-i tabletPort] [-F objFile saveFile] ...where the additional options not covered above are:
-g gPort
(largely obsolete) gPort names a device to use for the display. This was generally used in the past with dual-monitor systems, especially Sun systems in which the layout display might go to /dev/fb.-i tabletPort
(largely obsolete) tabletPort names a device to use for graphics input. This has not been tested with modern graphics tablet devices. It is ignored by the X11 and OpenGL display interfaces.-F objFile saveFile
(largely obsolete) Create an executable file of the current magic process, a core image snapshot taken after all initialization. objFile is the name of the original executable, and the image will be saved in saveFile. This only works on VAXen and SUNs running an old SunOS (using a.out executables).
The Tcl version, especially using the console, can make debugging runtime errors difficult, especially if the error appears in the console and then the console is destroyed along with the interpreter as magic exits suddenly. Also, the convoluted way magic starts up under the interpreter means that some reported errors may not actually point to the correct origin of the error.The methods described below progress from easiest to most difficult, but each can be useful depending on how and when the program bites the dust.
gdb "attach" method
The easiest method to debug magic is to use the "attach" function in gdb, which can be specified on the command line as:gdb program ppidIf only one process using the Tk wish graphical shell is running, the following Linux shell command (which can be copied into a shell script, for convenience) will attach and run gdb on the magic process:gdb program `ps -C wish --no-headers -o "%p"`Although this is supposed to work according to the manual page for gdb, I find that gdb doesn't recognize any symbols unless I do:ps -C wish --no-headers -o "%p"using the result of the first command for process_id in the gdb attach command. On machines that don't recognize the "-C" switch to ps, use whatever variant that will show you the process ID of the "wish" executable.
gdb wish
attach process_idNote that once gdb is running, the program may be interrupted at any point with a control-C key sequence in the terminal running gdb, to check variables, calling sequences, set breakpoints, etc. The gdb command "continue" resumes the program after attaching the debugger to the process. If you want the magic developers to investigate a segmentation fault, run the program under the debugger using the above method, and try to repeat the minimum number of steps leading to the crash. After the crash condition has caused the process to drop back to the debugger prompt, run the command "where" to get a stack trace of the subroutine call stack. Email this information to the developers, along with any other relevant information.
If the program fails during or after loading the technology file, but does not crash, it is still possible to use this method by attaching gdb, setting a breakpoint, then running
tech load tech_namefrom the magic command line. The tech load command clears out most of the allocated memory structures used by magic and regenerates them from scratch as the technology file is loaded back in.If the program crashes too fast to attach gdb to the running process, then one of the methods below may be necessary.
"noconsole" method
Errors which disappear along with the console can be viewed by running magic without the console:magic -noconsoleTo debug more pernicious runtime errors, it may be necessary to do a partially manual startup of magic. For non-fatal errors (i.e., an exit with an error but not a segmentation violation or bus error), do the following:wishNote that with this kind of manual startup, it is not possible (or at least, it's not easy) to use the "tkcon" console window.
source /usr/local/lib/magic/tcl/magic.tcl
standalone method
Sometimes it may be necessary to pass arguments to magic. An example follows:wish
set argc 4
set argv {-d OGL -T scmos}
source /usr/local/lib/magic/tcl/magic.tclmanual object load method
Under some circumstances, it may be necessary to manually load the magic shared object file to figure out what went wrong. This is a good thing to do if, for instance, magic reports that it can't find the "tclmagic.so" file:wishFor fatal errors (crashes), do the following:
load /usr/local/lib/magic/tcl/tclmagic.so
magic::startgdb wishVarious combinations of the above tactics may be necessary to get the program to run in the right mode for reproducing the runtime error. Note that all of the examples above assume that magic has been installed in the default directory /usr/local, and proper substitutions should be made if required by a non-default location of the installation.
run
source /usr/local/lib/magic/tcl/magic.tcl
This version IS listed in the section above as "BETA" code, and as such, no guarantee is made to its stability. BETA code should not be presumed to generate a perfect result, though, and all final output should be checked against a separate layout tool. Given the expense of fabrication, even DISTRIBUTION code should not be inherently trusted without at least an eyeball check by an experienced layout designer. Magic 6.5.1 is DISTRIBUTION. Magic 7.1 and Magic 7.2 are BETA. Magic 7.3 is ALPHA.More designations: Magic 7.1 "NONMANHATTAN" option is BETA. Magic 7.1 "FILE LOCKING" option is correct in the 7.1 CVS source code and later versions, but there is no need to compile with it unless you expect more than one person at a time to be working on a layout. It may be considered BETA. New magic techfiles from ISI (MOSIS) have their own designations and are currently described as BETA. Old magic techfiles "scmos.tech27" and its ilk are DISTRIBUTION for most purposes such as small digital circuits (college class projects and such) but are getting outdated.
Note: When checking magic output for errors, remember to always check the CIF or GDS result, as an improper technology file can introduce new errors into a layout which are not checked by either the magic extraction or the DRC rule-based checker. Because errors may also exist in the DRC section of a techfile, a layout ideally should be checked against a professional-grade DRC checker such as CALIBRE.
The purpose of the recent Magic development effort is, eventually, to be able to call Magic a "professional-grade" tool. Any help in this effort is greatly appreciated.
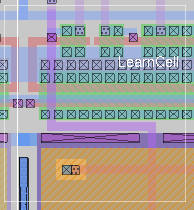
Shows off a number of features of the Tcl version, including the cell manager window, the tech manager window, the toolbar, the console command-line entry window, and popup dialog boxes. Also shows off the version 7.1+ features of the OpenGL display and the non-Manhattan geometry extension.
- Original (prior to adding revision information); last updated August 29, 2002. Changed the "make" method from "make wrapper" and "make install-wrapper" to "make tcl" and "make install-tcl" both to reflect the fact that SWIG is no longer used, and to make it more syntactically compatible with "tclspice".
- Fixed conflicting routines in "exttospice" and "exttosim"; "exttosim" can be run without crashing the program. Extraction output now redirects to the console output, not the terminal output.
- More "exttospice" and "exttosim" fixes: Both programs now free memory like they're supposed to. In addition, both commands can be run from inside a window and automatically operate on the root cell of the layout in that window.
- Extensions to the "magic wrapper" GUI ("magic -w"):
There is now a toolbar on the right-hand side of the layout window, showing all of the layers known to the tech file. Each one is a button. Clicking mouse button 1 paints that layer into the box in the layout. Clicking mouse button 3 hides the layer, and clicking mouse button 2 restores visibility of the layer. The name of the layer appears in the title bar of the layout. Also, the box coordinates are shown in the title bar. For people who use magic in 8-bit PseudoColor mode, the console window is repainted in magic colormap colors, so there is no more color switching between the layout and the console.- Important repairs to the CIF reading/writing and internal grid rescaling code---affects the ability of magic to read CIF/GDS in a different lambda scale from the scale at which it was written. Also, non-Manhattan geometry has finally been incorporated into the extresis code.
- Minor revisions thanks to Conrad Ziesler implementing the grid scaling code in the wiring and router sections, and a fix to some segmentation-faulting behavior, also in the router section. Fixed up behavior of the wrapper in all modes, including OpenGL and overlay planes. Unfortunately, it's my X server that fails on some of these mode combinations, not the magic code. The XFree86 server operates as intended, although it does not implement overlay planes.
- Added a menubar to the wrapper GUI. This includes file read/write functions, and a "cell hierarchy manager" that provides a tree-based view of cell definitions. New code changes allow magic to operate in a slave interpreter (specifically, as a slave interpreter in the TkCon console version). Changed magic command names to avoid conflicts with Tcl/Tk commands. Replaced the "list", "listall", "listtop", "parent", and "children" commands with an extended and more general method using two (new) commands "cellname" and "instance" (these are required by the cell hierarchy manager widget).
- Finished the basic GUI, including a working "cell manager" and "tech manager". Added general method for callbacks "magic::tag
" which replaces the previous method for handling captions and scrollbars, and allows syncronizing the GUI with command-line commands. Added new magic command "techinfo" to return several variables related to the loaded tech file. Added option "childinst" to the "cellname" command, which enables reporting the child instances of top-level cells, which are otherwise unavailable due to the fact that top-level instances are always named "Topmost cell in the window" and cannot be selected or searched by name. Added options "list" and "listall" to the three commands "cif istyle", "cif ostyle", and "extract style", so that the current style and available styles can be queried from the command line and returned as a Tcl result. Added "label", "subcell", and "error" layers to the toolbar. Added keystroke commands to the toolbar: "p" for "paint" and "e" for "erase". Switched mouse button functions so that button 1 = "see", button 2 = "paint", and button 3 = "see no" (hide layer). This matches the button 2 function in the tool bar to the function in the layout window, and works better for 2-button mice. - Added command "element" for annotations on the magic layout window. Presently, this is somewhat primitive. Commands are:
The name is a unique name given to each element so it can be registered and searched in a hash table. The style is the name of a magic style which must match the name from the .dstyle5 file (it can also be the number of the style, 0 through 255).
- element add rect name style llx lly urx ury
- element add line name style x1 y1 x2 y2
- element add text name style x y text
- element delete name
Also: Extended keystroke commands on the toolbar with: "s" for "select more area layer" and "S" for "select less area layer".
Also: Changed the "make" process so "make clean" descends into all modules, not just the ones selected by "make config".- November 18, 2002
Quick fixes on the tag mechanism (magic commands called from a command tag should not increment the sequence of command numbers, or else the "select" mechanism doesn't work right), and corrected the #ifdef statements in the proto.magic file so that interactive macros "p" and "l" (paint and label, respectively) are defined under the Tcl version.- November 19, 2002
Quick patch to revision 10, which crashes on any call to "select" with more than two arguments.- November 25, 2002
Completed the (initial version of the) tag mechanism, mainly with the option "element configure" which allows element positions to be changed, text to be altered, and styles to be added or removed.
Also: Added line antialiasing to the OpenGL version.
Also: Changed the outline rendering to do true outlines of layers rather than outline each tile. This allows, for example, nonmanhattan pads to be drawn without highlighting the entire internal tile structure.
Also: Changed the "techinfo" command (see above) to "tech info" and added a "tech load" command for real-time loading of the technology. This can be used to develop and reload debugged/extended versions of the same tech file, or to load an entirely new technology. This is still under development, is inherently dangerous, and can crash the whole program.- December 2, 2002
Completed the "tech load" command so that it does not complain or crash the program, although existing layout may be invalidated if the number of planes changes.
Also: Extended the "image create layer" method under Tk with the ability to drop entire layouts into Tk images. The syntax is "image create layer-name -width -height ", where "window_name" is the Tk path of an existing layout window. The existing window will be deleted when the image is instantiated. - December 9, 2002
Completed a reasonable first draft of the interactive IRSIM simulator under magic. This corresponds to IRSIM 9.6 Revision 1. Both programs must be compiled and installed for this method to work properly.- December 11, 2002
Added Mac OS X support (thanks to Michael Doster). Changed the "layers" command to "tech layers", with "tech layers *" vs. "tech layers" differentiating between the version which returns a Tcl list of all canonical names and the one that prints all names and aliases, respectively. Started a skeleton program for the techfile builder wizard, added a minimal-size techfile ("minimum.tech27"), and debugged the operation of magic under the minimum techfile.- December 12, 2002
Correction to scmos/Makefile which deletes "minimum.tech27" in rev. 15 and thus halts the make install process.- December 16, 2002
Minor corrections for OS X support when not compiling with Tcl/Tk support (again, thanks to Michael Doster).- December 17, 2002
Changed the tech initialization routine to use memcpy() and memset(). This takes a couple seconds off of startup when magic is compiled without optimization (which is the default for magic 7.2, as long as it remains in alpha status).- December 23, 2002
Finally changed the way tech styles are handled so that magic can take more than 64 layout styles, and is not dependent on the ordinal numbering in the styles file. Styles may be called out by name as well as number in the "styles" section of the technology file. Modified the OpenGL dstyle file to take advantage of the new system.
Also: Removed a lot of old cruft from the distribution, including AED and X10 graphics packages, the "mpack" command, magic's built-in malloc() routine, and the VAX-only executable image "freeze" and "thaw".
Also: Did a test with the "plow" section in which the feature is modularized under Tcl, is not loaded on startup, but auto-loads the first time the feature is requested (by executing the "plow" or "straighten" command). The plan is to extend the modularization to the "plot" and "route" sections.- January 6, 2003
Fixes to the extresis geometry extraction and subcircuit boundary handling. Fixed modularization for the "plow" option and extended modularization to the "plot" and "route" options.- January 7, 2003
Due to an error, revision 21 was exactly the same as revision 20.- January 8, 2003
Quick fix to the install process, which was missing the glyph files in the graphics subdirectory. Thanks to Tim Chuang for reporting this error.- January 20, 2003
Added a window console option, although the implementation is only partial.- Feburary 10, 2003
Rewrote the graphics routines to find display depth during display initialization. This corrects an error left around since the display style file format was changed. As a result, it is no longer necessary to declare the display depth in the display style file. This is fortunate, since which style file is read depends on the display depth! I have tested Tcl and non-Tcl versions in X11 and OpenGL at display depths of 8, 16, and 24, and everything appears to work correctly. Also, fixed the colormap repainting of the Tk console in 8-bit pseudocolor mode, which was broken since I switched to a master/slave interpreter configuration with the console.- February 19, 2003
Reincorporated the 3D graphics from the 3D version into the main distribution as a "specialopen" type window. The interface remains somewhat crude, but the command "specialopen wind3d" will bring up an OpenGL 3D window, and various keys manipulate the view: the top keyboard row (numeric keys '1' through '0', minus ('-'), and equal('=')) manipulate the viewing' angle. Keys 'Z' and 'z' zoom out and in, respectively. Keys '>' and '<' change the relative z-axis (height) scaling. Arrow keys reposition the view (albeit relative to the original, top-down view).- February 24, 2003
Extraction changes: Tech file now takes keywords "device" which takes the place of the "fet" keyword (although that is kept for backward compatibility). Device names are: "mosfet", "bjt", "capacitor", "resistor", and "subcircuit". In particular, the non-FET devices output relevant information to the .ext file, including total capacitance for type "capacitor" and total resistance for type "resistor". "device mosfet" differs from "fet" in that values for gate length and width are written to the .ext file instead of area and perimeter. While the current code keeps the simplistic relationship between area and perimeter and length and width, technically this change allows a more sophisticated extraction implementation which would correctly handle non-standard devices such as annular FETs.
Enhancements to 3D graphics: Key "C" will toggle between magic layout and CIF layout views.
Layout window client command "cursor" added which returns the instantaneous value of the pointer in magic coordinates.- February 26, 2003
Minor bug fixes to non-Tcl compilation; "config" script changes for Solaris support, and "config" script support for Tcl/Tk in non-standard directories, especially for Mac OS X support.
- March 4, 2003
Repaired all the problems with Mac OS X support for the Tcl/Tk-based version, and a couple of other glitches associated with "make config" in Revision 27.
Also: Removed all format version numbers from magic's system files: .dstyle6 becomes .dstyle, .cmap1 becomes .cmap, and .tech27 becomes .tech. Each of these files except cmap (which has only ever had one format) takes a keyword "version" with the version number, internally. Future versions of magic should read the format version inside the file and adjust the read routine to match the format. Current format ".tech27" is tried as alternative name if a ".tech" file cannot be found, because there are so many ".tech27" files in existance which do not belong to the magic distribution.- March 10, 2003
Major changes to the "make config" file for support of Tcl/Tk in non-standard directories; hopefully this version is compatible with Cygwin, Solaris, and Mac OS X, although a lot of configurations are untested and it may take some feedback before everything is working reasonably well. Part of the make process changes includes having the linker export only required symbols (procedure names and global variables) to avoid conflicts with other dynamically-loaded object files.
Also: Commands "exttospice" and "exttosim" have been changed so that they are recognized by magic as built-in commands (that is, they have an entry in the command table and show up in the "help" list).- March 12, 2003
Removed "plow" from the list of module choices (or any choices) because the plow section of the tech file is used by the "stretch" command. Lack of the plow module changes magic's behavior, so it should always be installed.
Also: Reinstated the "-namespace-flat" and "-suppress undefined" switches for Mac OS X, because the use of the version script apparently makes it necessary.- March 23, 2003
Finally implemented an apparently-correct procedure for handling overloaded commands. Commands "array", "load", "flush", and "label" have been reverted back to their original forms. "clockwise" can be used as "clock" without generating an error. "grid" remains renamed to "gridspace".
Also: Attempted a fix to user-input function TxGetLinePfix(), but so far this is still broken (it works from the command line, but not internally).
Also: Fixed the "goto" command so that it works on internally-named nodes (it was never updated when the way internal node names are generated was changed).- March 26, 2003
Fixed some errors in the new "device *" extraction method (old "fet" record was not backwardly compatible as it was supposed to be, and the "device bjt" order of arguments was incorrect).
Also: Added a method to subcircuit extraction in which labels can be suffixed with "#n", where "n" is the order in which the port should be written to the subcircuit record in the SPICE output. This allows ports to be specified to match a pre-existing SPICE subcircuit, rather than forcing the user to make the subcircuit match the SPICE output from Magic.
Also: Fixed a string allocation error in the Tk/TOGL graphics routines which would cause occasional fatal crashes.
Also: Fixed some errors in the CIF/GDS read routine to prevent arithmetic overflow. This repairs some, but not all, cases.
Also: Fixed the previous fix for the Mac OS X compile. Thanks to John Geisz for helping with the Mac OS X compile and install problems.- March 31, 2003
Extensions to the "box" and "array" commands. Both commands now take numerous options. Do "box help" and "array help" for a complete list of options.
Also: Reinstated the original "grid" command (instead of the rewritten "gridspace" command). Also: Wrote in a lot of application interoperability code (scripted). Other applications are invoked on the Tcl command line as they would from the shell command-line. For instance, invoking IRSIM is now done by typing "irsim" at the Tcl prompt, not "startirsim". All applications accept their usual command-line arguments.
Also: More changes for Mac OS X compile and compatibility. Possible problems have been seen with recent OS X revisions which have apparently enabled 8-bit overlays, but may have different values for reserved portions of the colormap. A temporary fix is to set the shell environment variable "MAGIC_COLOR" to "24bit" to force 24-bit mode, or to set "X_COLORMAP_BASE" and "X_COLORMAP_RESERVED" appropriately, probably to 0 and 2, respectively (this is a guess).- April 7, 2003
Extension to transistor extraction to include support for annular transistors.
Also: Important fix to the non-Manhattan paint function. The bug apparently only affected CIF/GDS file reads (layers with non-Manhattan geometry would occasionally get painted with the wrong magic layer type). Also for CIF/GDS reads, added an internal grid subdivision limit so that the internal grid doesn't get subdivided so much that integer overflows occur on large coordinates.
Also: Added backslash-r and backslash-b (linefeed and backspace) handling to TkCon for compatibility with tclspice output.- April 15, 2003
Important fix to two outstanding problems: 1) The CIF "bloat-or" function for writing CIF output now handles non-Manhattan geometry, enabling output for non-Manhattan transistor geometries (such as annular devices in submicron technologies); 2) The "widespacing" DRC rule has been implemented in a robust way (the previous version was a bit of a kludge and didn't catch all errors). It remains to be determined how this implementation differs from Dracula or other DRC checker implementations. The DRC rule syntax iswidespacing layers1 width layers2 spacing adjacency whyfollowing the syntax of the "spacing" rule except for the addition of "width", specifying the width of material in layers1 which triggers the additional spacing rule.
Also: Added cell deletion and cell renaming in the form of "cellname" subcommands in the following syntax:cellname delete cellnameThese functions currently do not support the file locking feature; that is, it is possible to screw up a shared layout database by using them. File locking support will be patched in in the near future.
cellname rename cellname newname
Also: Fixed a bug preventing compilation of the non-Tcl version in revision 34.
Also: Partially implemented autoconf by attaching the OS and hardware auto-detect script "config.guess", and removing the user selection thereof from magic's config script.- April 16, 2003
Fixes a bad mistake in revision 35 which effectively disables "exttospice" and "exttosim", if they're compiled as modules (the default), and causes Magic to hang. Also fixes a bug found by James Adkins in which loading cells created by the "flatten" command will crash the program.- April 28, 2003
Introduced a real working autoconf, though probably will take some time to debug operating systems other than Linux.
Also: Revamped the "subcircuit" method, which deprecates the "subcircuit" boundary layer in favor of using the new port command to turn labels into ports. port help returns information on the correct syntax.- May 5, 2003
Incorporates a LEF output module for defining characteristics of a circuit relevant to standard-cell place-and-route. The port command has been extended to include use and class designations. A new command property has been added to assign key-value string pairs to a cell, which can be saved and reloaded along with the layout. A new command lef has been added to generate LEF-format output for a cell. Each of these commands implements a help option for more information.- May 19, 2003
Enhanced, corrected, and expanded three-dimensional viewing under Tcl/Tk + OpenGL with the "specialopen wind3d" command. Fixes to the LEF module after testing on 3rd-party tools. GNU "autoconf" compilation tested on Linux and Solaris. Fix to extract section for a long-standing error (exists in v.7.1) which miscalculates perimeters of ndiffusion.- June 11, 2003
Fix to annular and nonstandard transistor extraction. Fix to Solaris autoconf make script.- June 20, 2003
Fixed the scrollbars in the Tk GUI. Extended the syntax of command "scroll" to include scrolling by layout units. Added capability of the wind3d "specialopen" window to be generated as a Tk path, and added the "magic::render" command to the Tk GUI with a (trivial) GUI wrapper as a proof-of-concept. Added "target window" option to the cell manager. Changed GUI so that the toolbar is not shown by default, but is chosed from the (new) "Options" menu. Removed "Cell" and "Tech" menu buttons and moved them under the "Options" menu as checkbuttons. Fixed an error in which the scrollbars in the non-Tcl version did not recognize mouse input. The fix substantially cleans up the "WindSend" routine.- July 10, 2003
Changed some CPP processing to M4. Changed extract extension for "device resistor" to include the SPICE type "semiconductor resistor". The semiconductor resistor syntax is used unless the name argument is "None", in which case the simple resistor is used. Changed the keyboard behavior so that shift-keypad keys are not interpreted as ASCII numbers.- July 16, 2003
Fixed "magic/symbol.map" so that exttospice and exttosim work again; other bug fixes related to the modularization of the command tables. Added a preliminary "cif warn" option; esp. with "cif warn align", the layout can be checked for contacts on half-lambda spacing. Fixed feedback rendering so that it does not attempt to draw out-of-bounds entries. Fixes and updates to the gnu autoconf interface.- July 24, 2003
Changes to the Tk graphics to replace X11 calls by Tk calls whereever possible. Added automatic grid scaling for GDS file reads, and added some useful options to CIF and GDS reads, including limiting and redirecting error and warning messages.- August 4, 2003
More fixes stemming from the modularization of the command tables. Also: Added configuration changes necessary for compiling an RPM package from the Magic source (enhancements courtesy of Erwin Prin).- August 8, 2003
Reformed the electrical connectivity search function to be a one-pass, recursive function, avoiding redundant tile checks and speeding up the process. Added the ability to search connectivity across ports, for ports having the same index. This search function modification has not yet been copied to the "extresis" and "sim" functions.- August 14, 2003
Fixed a bug in the new electrical connectivity search function, and extended the improved search function to "extresis" and "sim" (e.g., "getnode") functions. Also: Added files pertaining to the creation of an RPM package for Magic, courtesy of Erwin Prinz. These have been placed in a new subdirectory scripts/rpm.- September 5, 2003
Fixes/enhancements to the file locking code, courtesy of Mike Godfrey.- September 12, 2003
Switched from the "varargs" method for variable argument subroutine calls to "stdarg", in response to GNU gcc no longer supporting the former.- September 22, 2003
Changes to handling of standard cells during extract and exttospice. Also: Fix to capacitance value output from the "device capacitor" extraction method.- September 26, 2003
Added a LEF file reader to Magic ("lef read file"). Fixed the connectivity algorithm which searches across ports with the same index (which is critical for handling pins with multiple, unconnected ports read from a LEF file).- September 30, 2003
Corrected a serious CIF/GDS output problem: Contacts may not be centered if the contact size or spacing is an odd number of centimicrons, because half-centimicron values get rounded, and may cause the output geometry to be off-grid. It may also cause overlapping contacts in subcells to produce contact cuts at different positions.- October 3, 2003
Added a DEF file reader to Magic ("def read file"). Changed the behavior of the "cellmanager" widget in the Tcl wrapper so that it remains nonexistant until called from the Options menu. This prevents magic from hanging while the cell manager processes thousands of cells if a large design is loaded in.
Note that the LEF and DEF syntaxes have been only partially implemented. In particular, wire widths on routing layers are ignored and a default wire width of 3 is used. Layer names in the LEF and DEF files must have entries in the technology file; that is, they must be included as aliases for magic layer names. Eventually, this should migrate to a new section for the technology file.- October 27, 2003
A number of fixes, including the graphics handling of layer perimeter outlines, a fix to the "cif limit" syntax parsing, an important fix to CIF read-in for files that define the geometry in sub-centimicron units, and an error reported by Wai Yung in which compilation fails if nonmanhattan extensions are disabled. The LEF and DEF readers have been substantially fixed and enhanced.- November 2, 2003
Changes made for compilation on an AMD Opteron (using RedHat GinGin64). Operation appears to be correct. Compilation produces numerous warnings, but no errors.- November 12, 2003
Minor fixes to LEF and DEF read-in routines; cap on wiring contact types removed.- November 16, 2003
Major changes to LEF and DEF input method for better handling of large (greater than 1GB) files.- November 25, 2003
Major changes to the techfile format. Format number incremented to 29. Format 29 adds the asterisk (*) notation for any layer to indicate the union of that layer and all contact layers which have that layer as a residue. Use of this notation SIGNIFICANTLY decreases the size and complexity of the technology file, as well as increasing readability. Also, added several extra types for DRC checking. These are all essentially duplicating the functionality of the "edge4way" rule, but make the DRC section of the technology file easier to read. New DRC checking types are "surround", "overhang", and "rect_only".- November 28, 2003
Includes a fix to the IRSIM handling routine, which was doing I/O incorrectly for SYSV-style select() calls. Thanks to Mike Marcel for pointing out this error. Also, the CIF parsing of the "*" notation (see above) required restricting to the plane of the layer.- December 1, 2003
Colormap and style file changes to add colors and styles for metal layers 9 and 10 and corresponding vias. Also, changed label handling in the LEF file reader for speedup reading files with many labels (i.e., complicated port geometries).- December 23, 2003
Additions to the LEF/DEF reading for handling LAYER, VIA, and VIARULE statements. Also, changed the DRC parsing for the "edge4way" rule to determine the plane of "OKtypes", so that the optional 9th argument is not necessary.- December 30, 2003
Fixed a problem with DRC rule edge4way rule parsing stemming from revision 58. Also, corrected the non-autoconf compile (thanks to Jake Hill for reporting this problem). Finally, fixed the text input method for Tcl-based magic when used under the "tkcon" console. Now text entry works correctly with functions such as the netlist window's label input method.- March 11, 2004
Lifted the requirement that the Tcl version be compiled with "make tcl" and installed with "make install-tcl". "make" and "make install" now suffice for both the Tcl and non-Tcl versions.- March 19, 2004
Major changes!
Make changes: Autoconf compile now assumes options "with-tcl" and "with-opengl" are YES by default, checks for the header and library files for each, and disables them with a warning if something goes wrong.
Also: Corrections and extensions to the follwoing command-line functions: goto, findlabel, getnode, and the window command update. getnode now allows global nodename (labels ending with "!") to be disabled. The node alias reporting is fixed, and confusion over labels completely surrounded by a layer is fixed. The search routine SimTreeSrTiles has been overhauled for efficiency, with poor code excised. findlabel now has a "-glob" option to return a list of nodes matching a csh-style pattern with wildcard characters (this was already in Magic but only available under the Scheme interpreter). goto now has a "-nocomplain" option to prevent printing an error message if the node cannot be found (e.g., if it's a global node name). update command now has options "suspend" and "resume" to prevent and resume graphics refresh. This is useful when generating scripts to execute multiple commands.
Also: Added a new command search with syntax "search layers proc" which executes a low-level tile search for all tiles matching the layer list layers. For each tile found, it executes the TCL procedure proc, passing it a list of the tile lower-left and upper-right coordinates, and the tile type.
Also: Created a "pin list" GUI tool. This tool searches out all the pads in a design and generates a pinout list. The tool can be used to aid in renaming all the pads.
Also: Rearranged the source directory structure so that all TCL scripts go into the subdirectory "tcltk".- March 31, 2004
Modified the tech file parser to handle DOS-style carriage-return/linefeeds.
Also: Modified the "squares-grid" cifoutput function to avoid writing contact cuts with less than the specified border. Added an optional y-grid value to the "squares-grid" function. This allows the generation of interleaved rows or columns of contacts, such as required for pad generation in some processes.
Also: Fixed an error in the DBResidueMask(), which caused the new "*" notation for the technology file format to produce incorrect lists of layer types. Also: Extended the cmdParseCoord() routine to handle coordinates on the user grid (specified by the "grid" command). Previously, "snap grid" only worked for mouse motion. It now works correctly for all commands (and, consequently, all key macros), e.g., move, stretch, etc.- April 9, 2004
Modified the makefile process for compatibility with Cygwin, and moved tclmagic.c to the tcltk directory as the easy way to avoid an error in trying to compile a library file for the module.- April 12, 2004
Modified the exttospice (ext2spice) routine to output a .subckt ... .ends record around the netlist output of top-level circuits containing ports. This action can be subverted in the TCL version with the command "exttospice subcircuit top off". Values are "off", "on", and "auto", with the default being "auto".- April 29, 2004
Extraction of overlap and sidewall capacitance was modified to force it to subtract the substrate capacitance computed for overlapping types belonging to the same electrical node. Also, as magic does not appear to compute overlap between plane images of a contact, only one contact image can declare an area capacitance to substrate. This is NOT all worked out properly.- May 7, 2004
Corrected a number of errors in the search functions when the database contains non-Manhattan tiles. In particular, some searches would go into an infinite loop (interruptable, but still annoying).- May 13, 2004
Corrected search routines over non-Manhattan geometry in the routines used by "getnode" and "extresis". These instances were missed in the Revision 69 fix.
- The "make config" process has been redesigned so that the interpreter (None, Tcl/Tk, or Scheme) option is offered at the beginning. Modular options are only prompted if they are available.
- Option THREADS is available for fully-threaded graphics handling in both X11 and OpenGL. This avoids the use of a forked "X11Helper" program, so it cannot be left around as a detached process.
- The ~cad "cad user" directory and associated directory structure is obsolete. It was rather unorthodox to begin with. Now magic relies entirely on the variable $CAD_HOME. A default value for this variable is set as the first prompt to "make config"; the directory so specified is the target root directory for installation. "/home/cad" is suggested if it exists, for reasons of backward compatibility; however, use of something more obvious like "/usr/local" is encouraged. Setting environment variable "$CAD_HOME" overrides the default value, as in previous versions. Installation to user directories is trivial (for those without root access, or those who want, for understandable reasons, to keep the ALPHA code in a relatively benign place and not overwrite existing, working versions of magic).
- OpenGL graphics have been fixed for use with multiple layout windows open at the same time. Slight single-pixel differences in positioning of boxes and rectangles due to OpenGL's different coordinate system has been (mostly) fixed.
- CIF writes to any precision, including nanometers, so is appropriate as output for deep submicron processes. Deep submicron is better handled so that scale factors in the tech file can be specified appropriately: "scalefactor 6.5" works for 0.13-micron processes, with cif grow/shrink factors listed in centimicrons; alternatively, "scalefactor 65 nanometers" works for 0.13-micron processes with cif grow/shrink distances listed in nanometers. The "calmaonly" keyword is deprecated. Note that not only are odd numbers allowed for the scalefactor, but also floating-point.
- The optional "reducer" keyword is ignored for the cifoutput scalefactor entry. CIF output is reduced by the maximum amount possible, and this is computed automatically by checking the greatest common factor among all the CIF output grow, shrink, bloat, and squares factors.
- The restriction that the magic internal grid must be equal to lambda has been lifted. This is the default, but it can be changed using the (new) "scalegrid" command, if higher or lower resolution is required. In addition, the "snap" command has been redefined so that the cursor can be made to snap to either internal units ("snap internal") or lambda units ("snap lambda"). Snapping occurs only on mouse-based actions. Command-based actions such as "bbox" and "move" always have units specified in lambda. However, units are not restricted to integers, so movement in internal units can be specified by floating-point distances ("move w 3.1").
- CIF input automatically takes care of internal vs. lambda grid scaling so that no information is lost in CIF/GDS reading due to input coordinates specified in fractional lambda coordinates. Magic file output is scaled to the largest scale which keeps all measurements on integer boundaries, so files do not tend to continuously fracture themselves into tinier and tinier internal units.
- A new command port turns labels into "ports", allowing special handling of cells as subcircuits with respect to extraction and simulation. Cells containing ports are extracted, but this extraction is ignored by "ext2spice", which treats the cell as a "black box". "ext2spice" generates an "X" (subcircuit call) record in place of the cell, with the arguments in the order that the ports are declared (use port help for usage information). This is a useful and powerful way to handle all sorts of situations from standard cells (where a pre-characterized simulation model may be preferred over magic's own extraction) to resistors, capacitors, inductors, and any special geometry with unusual features which cannot be handled by magic's extraction algorithm.
Note: This replaces a method introduced in one of the early revisions of 7.2 in which the ports were identified by the coincidence of a layer called "subcircuit" and labels in the cell. The new method is a response to complaints about the ugliness of the "subcircuit" layer method. Any layout generated with the earlier method should update by hand-editing the .mag files, removing "subcircuit" layer sections, and adding "port" lines after each label which is intended to be a port.- In conjunction with the "subcircuit" method, the "extresis" command has been extended to include the command "extresis geometry". When this is selected, subsequent execution of the command "extresis" will generate a geometry file in place of each cell with ports. This geometry file is in the format of input for the "FastHenry" inductance field-solver program. It is appropriate for extracting values for spiral inductors and other RF structures.
- Colormaps and style files have been extended for use with up to 10 metal layers (up to revision 19, the top 3 metal layers overwrote some styles used by the MOSIS technology file set. As of revision 19, the handling of styles has been revised, the overwritten styles reverted to their original descriptions, and additional styles added for handling 8 metal layers and associated vias).
- Memory management has been improved. Now, only the current CIF input and output style and extract style are held in memory. Changing styles forces a re-read of the technology file. This change reduces memory overhead from 120MB to 27MB!
- Commands"cellname" and "instance" replace the commands "parent", "child", "list", "listall", and "listtop". The command "cellname" expects a cell definition as an argument, whereas "instance" expects a cell instance name as an argument.
- A command "element" has been added for annotating the layout. The main purpose of this is to allow other programs to display information back onto the magic layout (IRSIM does this, but using its own method. This method is more general and not restricted to IRSIM). Presently the "element" command supports rectangles, lines, and text, although styles are limited to magic's known styles from the ".dstyle5" file. Option "element configure" can be used to change element position, change text, or add and delete styles. Note that with elements, styles are drawn in the order they are added to the element, not in numerical order of the style index, as they are in the layout. Option "element names" returns a list of all the known elements, and "element inbox" returns a list of all element which are found within the confines of the edit box's current position.
- A new command "tech" basically replaces and extends the wizard command "showtech" (which still exists). In particular, several options (do "tech help" for a complete list) returns various properties of the technology. A new option "tech layers" now replaces the magic "layers" command. The syntax "tech layers *" vs. "tech layers" differentiates between returning a list of all canonical layer names and a list of all names plus aliases, respectively. The wildcard character is in keeping with the "tech layer name" syntax which returns the canonical name of layer name or alias name.
"tech load filename" reloads the technology file or loads a new technology file. This was introduced in version 7.2.12 and does little checking against the previous technology, so it can really foul up an exising, loaded layout. Mainly intended for use in debugging new technology files. Beginning with Revision 31, the option "tech load filename [-noprompt]" is available, which is useful for including in a project directory's .magic file, to force loading of a specific technology file.- As of revision 12, version 7.2 renders outlined layers by drawing the border around the layer instead of drawing a border around each tile. This allows, for example, non-square contacts and beveled-corner pads to be drawn without filling in all the internal tile structure.
- Revision 19 changes the way the display style file is written, and moves from "dstyle5" to "dstyle6". The new style file is divided into three sections, "display_styles", "layout_styles", and "pale_styles". Each section is numbered separately. The "display_styles" section is the part containing the built-in styles for things such as the cursor box, highlighting, feedback, window border drawing, and defining a palette of solid colors. The order of these styles is fixed, as the ordering is hard-coded into the magic source. The "layout_styles" section defines the set of styles which can be used for layout types. The ordinal number (first column) for the style is backwardly-compatible to past technology file versions, which declare style by number only. However, the numbers do not need to be in ascending order, and styles may now be inserted between existing styles. The numbers assigned to existing styles should not be changed, though, to retain the backward-compatibility. The "pale_styles" section defines all of the styles used to draw layout in non-edit cells. Typically these are defined to be lighter or "paler" versions of the styles defined in the "layout_styles" section. The entries in the "pale_styles" section must match the entries in "layout_styles" one-to-one (this restriction may be lifted in the future).
- Revision 14 introduces the "techbuilder" Tcl script. This is now a skeleton script to be worked on, but the general concept is a user-friendly interface to building new technology files from scratch, or modifying existing technology files. The primary intention is to hide the ugly and arcane details of the CIF input and output and the DRC sections, and at the same time produce a layout file which doubles as a complete design rule reference manual.
- Tcl/Tk. The major feature of version 7.2 is the incorporation of Tcl/Tk as not only the interpreter, but a replacement for both magic's terminal and graphics input and output. Tcl/Tk features are listed in the following section.
- Beginning around revision 50, magic has the ability to read LEF and DEF format files, and to write LEF format libraries. Implementation is limited in some respects but should be expanded as the need arises.
- The techfile format has been upgraded (now in format 29) for the purpose of reducing complexity and increasing readability of the file. New features are meant to discourage the use of preprocessing to generate the technology files. The asterisk notation (e.g., "*m1") indicates the union of the specified type and all contact types containing that type as a residue. DRC checking types "overhang", "surround", and "rect_only" duplicate edge4way functions, but are easier to read.
scmos8m.tech is an example technology file taking advantage of the new features.- The use of environment variable "MAGIC_COLOR" has been deprecated in favor of calling magic with "-d 8BIT", "-d 16BIT", or "-d 24BIT" to force a specific graphics mode (note that this is case-insensitive).
- The magic terminal and graphics input/output have been completely subordinated to Tcl/Tk. The magic prompt is a Tcl prompt; all Tcl commands may be executed from the command line. Magic commands may also be executed from the command line, although in some cases where magic commands have the same name as Tcl commands, the Tcl version of the command is forced to take precedence, and the magic version of the command must be specified with the fully-qualified namespace "magic::" prepended to the command.
- Some commands return values back to Tcl. Currently this has only been implemented for the "path" and "getnode" commands, but will be extended.
- "openwindow [cellname]" has been extended to "openwindow [cellname [windowname]]". Under Tk, "windowname" is a pathname for a Tk widget. The resulting window will be created but NOT mapped; it should be mapped with the Tk "pack" command. This allows windows to be generated inside an application frame, such as a GUI.
- Full-frame GUIs are facilitated by the added command-line argument "-n[owindow]" passed to magic on startup. This prevents an initial window from being generated. The calling application is then responsible creating all windows with the "openwindow" command.
- Commands have been extended to include the syntax "windowname magic_command". This allows any command to be directed at a specific layout window. For example, painting can be done in window ".magic2" by the command ".magic2 paint m1".
- The "TkCon" console window has been incorporated into magic. Magic may be run with or without the console (by executing script "magic" with or without argument "-c[onsole]"), but the TkCon console more faithfully reproduces the behavior of the original magic input/output, with the cursor indicating pending DRC checks, and implementing command-line history and automatic function completion. Commands can be entered from the layout window in either method, but with the TkCon console, commands can be partially entered in one mode and completed in the other. The TkCon also "pretty prints" the input and output, highlighting commands and variables with special colors, and painting error messages in red and other informative output in blue.
- "ext2spice" and "ext2sim" are incorporated as modules under Tcl, renamed to "exttospice" and "exttosim", respectively, and are loaded automatically. They become available from the Tcl command prompt as "magic::exttospice" and "magic::exttosim", respectively. These namespaces are "pushed" so that the commands may be executed simply by typing "exttospice" and "exttosim".
- The GUI-wrapper implementation has been aided by expanding the commands "windowcaption" and "windowscrollbars". "windowcaption" with no arguments returns the current window title caption. One argument, a valid Tk window, causes the magic layout window not to render its own caption but redirects the caption to the specified Tk window, which should be of a widget type that can accept the command "configure -text". "windowscrollbars" with two arguments, both valid Tk windows, causes the magic layout window not to render its own scrollbars, but redirects the window position information to the specified Tk windows, which should be Tk scrollbar widgets.
- The "setpoint" command, under Tcl, returns two point values (x y coordinates), one for screen coordinates, in pixels, and one for layout coordinates, in magic internal units.
- In 8-bit (pseudocolor) visuals, the layout colormap installs itself into the TkCon console window, so that the console maintains the same colors as the cursor moves between layout windows and the console. This greatly improves the use of magic in pseudocolor mode!
- Magic revision 14 re-incorporates the interactive IRSIM simulator into the Tcl version. See the section below on using IRSIM.
- Options "plow", "plot", and "route" are now modularized. They auto-load into memory upon execution of an associated command, and otherwise remain unloaded. The "make config" script allows each of these sections to be modularized (choice "module"), incorporated into the main executable (choice "yes"), or ignored (choice "no"). AT the moment, however, the command "specialopen netlist" does not auto-load the route module, as it should.
- When OpenGL graphics are compiled with the Tcl/Tk version, Magic has a new command "specialopen wind3d". This command brings up a 3D-view window (see screenshot, below). The 3D window has its own command set, accessible by typing the Tk window pathname (.magic3d) as a command. Type ".magic3d help" to get a full list of commands. The window also has a set of keystroke commands. Type "?" in the 3D window for a list of these keystrokes.
- The new command "search" allows low-level tile searches on a design hierarchy, using a TCL procedure as the callback function. The syntax is "search layers proc", where the search routine calls the TCL procedure proc for each tile in the design matching one of the types in the layer list layers. The TCL procedure will be passed five arguments, llx lly urx ury ttype, where the first four are the coordinates of the tile relative to the root cell, and ttype is the name of the layer type defined by the tile.
- The "Pinout List" tool aids in managing labels on the padframe. The pop-up window has three buttons. Search enumerates all the pads in the design and generates a list. The list shows up in the window; when any entry is selected, the pad area is selected and the window view changes to center on that pad. Edit semi-automatically generates and handles labels for the selected pad. Update recreates the pad list, reflecting any changes made to the "canonical" name of each pinout.
(See a screenshot of IRSIM 9.6 running under magic 7.2 with Tcl/Tk. The layout is the standard magic tutorial tut11a.mag and the setup was made with a slightly modified IRSIM command file tut11a.cmd, executed using the Tcl command source).
The IRSIM digital switch simulator was a casualty of the switch to the Tcl/Tk interpreter, until Magic 7.2 revision 14.The focus of the Tcl/Tk version of Magic is to take advantage of the interpreter's ability to load packages on the fly. The result is that disparate programs can run at the same time. Any program can call routines in any other program, although this is normally done via evaluation of interpreter commands.
To facilitate having other programs pass information back to magic for display, a new magic command "element" was added. This general-purpose method lets other programs print text, lines, and boxes on top of the magic layout.
To make use of IRSIM under Tcl/Tk-based Magic, it is necessary to have IRSIM version 9.6 Revision 1 or newer. IRSIM must be compiled with option "Tcl interpreter" and option "Tcl/Tk graphics". The "make" system on IRSIM has been changed to match that for "Magic". Values for "CAD_HOME" (requested at the beginning of the "make config" script) should be the same for both programs (nominally, "/usr/local").
IRSIM works in the following manner. IRSIM is, like magic, exttosim, and exttospice, compiled as a Tcl package, namely as a shared-object library (.so) file. There is a standalone script "irsim" which is normally in $CAD_HOME/bin. Invoked from the script, IRSIM runs under Tcl by itself, and can simulate from any ".sim" file, but cannot interact with magic layout. However, there is also a command "irsim" in magic. Invoked as "irsim", IRSIM loads as an additional package in the Tcl interpreter which launched magic. Able to dectect the "magic" package in Tcl, IRSIM then adds a group of commands designed for interaction between magic and IRSIM. The "irsim" procedure is smart enough to go looking for a ".sim" file matching the magic layout in the window, and generate one automatically if it doesn't exist. Because the IRSIM and magic packages share space in the Tcl interpreter, commands for both are available at any time from the command line. There is no switching between modes to access the simulator. The only caveat is that some IRSIM commands conflict with magic or built-in Tcl/Tk commands. These commands require a prefix "irsim::". For example, "clock" is a command used by Tcl to time the execution of procedures. To get the "clock" command in IRSIM, it is necessary to use "irsim::clock". Several IRSIM commands conflict with Tcl syntax, and so have been renamed. These are indicated below.
The IRSIM/Magic procedures defined when running IRSIM under Magic are as follows:
- irsim [param_file [cellname]]
This command runs irsim::start in a somewhat intelligent manner. If cellname is not supplied, it defaults to null. Under this condition, the toplevel cell in the magic layout window is assumed to be the one to be simulated. If param_file is missing, it will be substituted with the default value "scmos100.prm", corresponding to 1.0 micron technology.- watchnode [node_name [magic_color]]
This command causes IRSIM to display node values on top of the magic layout. With no arguments, "watchnode" expects a node to be (uniquely) selected in magic. It uses the magic "getnode" command to get the name of the node and map it to an IRSIM node name. The current value of the node is then printed on the layout, centered on the select box, and updated as needed by the simulation. If node_name is specified, IRSIM uses the magic "goto" command to find some valid label or paint in the layout belonging to the node, and displays the value there. magic_color is an optional color name from the "long names" column in the magic ".dstyle5" display styles file. If not specified, it defaults to "white".Note that node_name may also be an IRSIM vector name, in which case the magic "goto" command fails and the value is placed at the position of the magic cursor box.
- unwatchnode node_name
This erases the simulated node node_name from the magic layout.- movenode node_name
This command recenters the label for simulated node node_name to the position of the magic cursor box. This is useful if the value chosen by "watchnode" is in a poor position for viewing.- watchtime
This writes the simulation time in nanoseconds on top of the magic layout, placed at the position of the magic cursor box.- unwatchtime
Erases the simulation time display from the magic layout.- movetime
Recenters the simulation time display on the magic cursor box position.Entirely new IRSIM commands and procedures defined regardless of whether or not IRSIM is run under magic are as follows:
Results of "watchnode" and "watchtime" on the magic layout.
- start [-s] param_file sim_file
Because IRSIM is a Tcl package, it has an initialization function, which runs automatically upon loading, and a separate function which starts the simulator. This allows IRSIM to be loaded and ready to go before having a ".sim" file ready for input. The start command takes the same syntax as the standalone UNIX command prompt irsim command.- listnodes
This function makes a list of all the nodes in the (flattened) circuit. It is intended for use with a Blt-style "tree" widget allowing any node in the circuit to be found and displayed.- graphnode nodename [row [voffset]]
Display the value of node nodename on the "analyzer" display (a Blt stripchart widget). Note that due to the limitations of the Blt package, vectors cannot be specified for graphing display. The display can be divided into separate graphs (indicated by row, starting at zero, default = 0), each displaying any number of nodes. Nodes can be separated from each other by using voffset (default = 0) to add a constant offset to the node value on the graph. Nodes that are undefined (value "X") are drawn as halfway between LOW and HIGH values.IRSIM defines a callback function which returns values for all watched nodes and vectors on every update. This function is invoked as an extension of the IRSIM "display" command as follows:
The new Analyzer graph window under Tcl/Tk IRSIM.
display tclproc procedure_nameThe Tcl procedure procedure_name must be defined as a procedure taking exactly three arguments:proc procedure_name { name value tval } {IRSIM will call procedure_name once for each variable needing a display update, and fill the values for name, value, and tval. Argument name is the name of the variable (node or vector) to be updated. Argument value is the value of the variable (one character for nodes, or a character string for vectors). Argument tval is the time of the update. In order to facilitate the batch processing of all nodes and vectors which are updated at the same time value, procedure_name will be called once more after all variables have been updated, with the syntax
... (procedure body) ...
}procedure_name time t tvalThe procedure procedure_name should check for the condition "${value}" == "t" to differentiate this call from calls on node and vector names.IRSIM commands which have been renamed to accomodate standard Tcl syntax are as follows:
IRSIM commands which have been extended:
- restorestate replaces <
- restoreall replaces <<
- savestate replaces >
- querygate replaces !
- querysource replaces ?
- source replaces @
Currently (magic 7.2 rev. 61, IRSIM 9.6 rev. 10), there is no way to remove or reload a file being simulated by IRSIM. Fixing this is a high-priority item. Also, the ability to view bit vectors in the IRSIM "analyzer" window is incompatible with the use of the "Blt" package for graph displays, and will remain so until I create an analyzer package for use with Tk. I will not use the existing analyzer graphics, as they are horrid.
- assert node
- Short form. Without an assertion, returns the value of node node. This can be used directly in conjunction with magic to query the simulation value of nodes without adding them to the watch or display lists. To return the value of a layout node, select paint and do:
assert [getnode]Revision 5 corrects the function calling in Tcl such that it checks for the minimum/maximum number of arguments before passing the arguments to the irsim command handler. Previously, passing the wrong number of arguments to a command could potentially crash the program.
- Implement a better FET extraction method for resistors, corresponding to the method that handles annular transistors. Probably a good rule-of-thumb would be to use the "quick and dirty" method when a FET gate layer is restricted to only one tile (in which case (length, width) and (area, perimeter) pairs can be derived from each other, and use the more exhaustive method when more tiles are involved. Thus, fast processing would be ensured for most designs.
- Implement better handling of contacts in GDS output. GDS output size can be significantly reduced by putting contact cuts into subcells and arraying the subcell. This would be the domain of the "squares" function. However, GDS input should be able to flatten such instances to recover magic's composite form of contacts. This is a major issue, because magic's boolean operations on GDS and CIF input are done on a per-cell basis, so contact cuts in subcells which are missing layers can disappear entirely. Even when handled correctly by the cifinput section of the tech file, some configurations will turn into generic contacts and vias, not as easy to deal with as magic's composite contact areas.
- Correct GDS arrays. Magic arrays may be indexed from high to low numbers, which is not allowed in GDS. Such arrays need to be rotated in GDS output, with individual cells counter-rotated to match.
- Code cleanup. Code should compile cleanly when "-Wall" is added to the gcc compiler flags. See the "TODO" file. Note that many of these items have been done in magic version 7.3, leaving version 7.2 for a loss.
- Implement Timberwolf Place-and-Route as a Tcl-based program to interact with Magic.
- Implement an OpenAccess database interface to Magic.
- Introduce SPICE as the main interactive simulator under the Tcl/Tk version. This has largely been accomplished by Stefan Jones (MultiGiG, Ltd./Inc.) with tclspice, available from SourceForge.
- Get the "element" command working with feedback from SPICE (i.e., a more interactive interface to tclspice than is currently available).
- Make a few more changes to the colormap and style files. The colormap should declare color names; the style file should be able to use colors by index, by name, or by standard X11 name or #rrggbb notation.
- Extend the geometry extraction and inductance solving, with automatic generation of SPICE subcircuits from FastHenry.
- Further reduction of memory overhead can be achieved by rearranging the allocation of vectors and matrices in the ExtStyle structure. Right now, the memory savings doesn't seem to justify the effort of recoding all the affected files.
- OpenGL no longer hangs when multiple windows are present
- CIF input and output has been corrected for use with expansion factors such as the "nanometers" keyword.
- Memory overhead on startup has been reduced by almost 100MB, from 120MB to 27MB (Tcl/Tk takes up an additional several MB).
- Error in extracted perimeter values for n-diffusion nodes fixed.

| email: | 
|
Last updated: September 13, 2013 at 10:10am